Everything posted by Sandeep B.
-
How to Flush and Delete Postfix Mail Queue
This is short tutorial for clearing and deleting the mail queue from command line. Postfix is the mail server which is used to send mails, time to time there will increase in mail queue which contains failed email in order to check and clear the mail queue just run this following command from terminal/ssh. To check mail queue: mailq To remove all mail from the queue: postsuper -d ALL To remove all mails in the deferred queue: postsuper -d ALL deferred EXTRA : To delete or remove maildrop queues run this command : find /var/spool/postfix/maildrop/ -type f | xargs rm -rf SCRIPT : Also you can use this script to delete mail queue which contain certain keyword or email id : cd /root touch mailq-del.pl chmod 775 mailq-del.pl nano mailq-del.pl and add this below code in mailq-del.pl and save it : #!/usr/bin/perl $REGEXP = shift || die "no email-adress given (regexp-style, e.g. bl.*\@gmail.com)!"; @data = qx</usr/sbin/postqueue -p>; for (@data) { if (/^(\w+)(\*|\!)?\s/) { $queue_id = $1; } if($queue_id) { if (/$REGEXP/i) { $Q{$queue_id} = 1; $queue_id = ""; } } } #open(POSTSUPER,"|cat") || die "couldn't open postsuper" ; open(POSTSUPER,"|postsuper -d -") || die "couldn't open postsuper" ; foreach (keys %Q) { print POSTSUPER "$_\n"; }; close(POSTSUPER); example usage of script : cd /root ./mailq-del.pl example@gmail.com or ./mailq-del.pl keyword
-
Postfix add Dedicated Static IP per user for mail sending out CWP Linux Ubuntu
in this tutorial I’ll show you how you can assign user account ip for mail sending under postfix mail server. It will be good if you’re providing mail services to your use. Suppose you’ve one ip configured for mail server and a user who sends lots of spam or his/her website got infected and sending spam from the infected scripts this leads to main mail ip for email sending will quickly get into blacklisted and all other genuine users who are using safe practices for mail sending will suffer because of that bad user. To cope with this situation you need to have per ip basis configuration for user if one user ip get blacklisted then other users will not be affected and you can bait that bad user by disabling mail sending. Lets get started with the configuration before you configure ensure you’ve Multi ips are attached in your server network. Create file called sdd_transport_maps.regexp in /etc/postfix/: /@user1-domain\.tld$/ username1: /@user2-domain\.tld$/ username2: /@user3-domain\.tld$/ username3: replace /@user1-domain\.tld$/ with domain.tld eg : /@alphagnu\.com$/ replace username1 with account username alphagnu you can add like this for multi users and domains. Now In /etc/postfix/master.cf create and add special transport lines called user1, user2, user3 and more user as per need : username1 unix - - n - - smtp -o smtp_bind_address=10.10.10.1 -o smtp_helo_name=user1-domain.tld -o syslog_name=postfix-username1 username2 unix - - n - - smtp -o smtp_bind_address=10.10.10.2 -o smtp_helo_name=user2-domain.tld -o syslog_name=postfix-username2 username3 unix - - n - - smtp -o smtp_bind_address=10.10.10.3 -o smtp_helo_name=user3-domain.tld -o syslog_name=postfix-username3 Replace smtp_bind_address ip with the dedicated ip for the user account. eg : alphagnu unix - - n - - smtp -o smtp_bind_address=10.10.10.1 -o smtp_helo_name=alphagnu.com -o syslog_name=postfix-alphagnu In /etc/postfix/main.cf add sender_dependent_default_transport_maps line: sender_dependent_default_transport_maps = regexp:/etc/postfix/sdd_transport_maps.regexp reload/ restart postfix service postfix restart that’s it you’re done configuring it test by sending email.
-
Clean all log files and Free DISK Space in CWP – Control WebPanel
hi search the `sh` binary location by typing : which sh it will output the binary path location replace with /usr/bin/sh by the way sh location is always in /usr/bin/sh in centos
-
CWP Apache enable TLS 1.3 - Control Web Panel
the image can be for old apache, you can choose the latest version and edit the option for apache tls 1.3 + brotli + http2 install the brotli Installing Brotli on your server: yum install pcre-devel cmake -y cd /usr/local/src git clone https://github.com/google/brotli.git cd brotli git checkout v1.0 ./configure-cmake make && make install Adding path for brotli dependencies files (run this commands one by one): grep "/usr/local/lib/" /etc/ld.so.conf || echo "/usr/local/lib/" >> /etc/ld.so.conf ldconfig Then you need to edit the configure option after you downloaded the https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/apache-rebuild-new7.sh or https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/apache-rebuild-new8.sh i.e. edit the file and add this config flag at last of "./configure" line : --enable-brotli --with-brotli=/usr it will look like below ./configure --enable-so --prefix=/usr/local/apache --enable-unique-id --enable-ssl --with-ssl=/usr/local/opensslso --enable-ssl-staticlib-deps --enable-mods-static=ssl --enable-rewrite --enable-deflate --enable-suexec --with-suexec-docroot=/home --with-suexec-caller=nobody --with-suexec-logfile=/usr/local/apache/logs/suexec_log --enable-asis --enable-filter --with-pcre --with-apr=/usr/bin/apr-1-config --with-apr-util=/usr/bin/apu-1-config --enable-headers --enable-expires --enable-proxy --enable-rewrite --enable-userdir --enable-http2 --enable-brotli --with-brotli=/usr then run the bash script : chmod 755 apache-rebuild-new7.sh sh apache-rebuild-new7.sh or chmod 755 apache-rebuild-new8.sh sh apache-rebuild-new8.sh then follow the required configs listed here from After Apache is rebuilded create the config file
-
CWP Apache enable TLS 1.3 - Control Web Panel
hi tutorial is posted here :
-
CWP Apache Enable mod_brotli Brotli Compression - Control Web Panel
Brotli compression for Apache will save you from slow compression speed as it uses latest compression technology developed by google. The mod_brotli module provides the BROTLI_COMPRESS output filter that allows output from your server to be compressed using the brotli compression format before being sent to the client over the network. This module uses the Brotli library found at https://github.com/google/brotli. Follow the installation procedure steps to install mod_brotli :- Installing Brotli on your server: yum install pcre-devel cmake -y cd /usr/local/src git clone https://github.com/google/brotli.git cd brotli git checkout v1.0 ./configure-cmake make && make install Adding path for brotli dependencies files (run this commands one by one): grep "/usr/local/lib/" /etc/ld.so.conf || echo "/usr/local/lib/" >> /etc/ld.so.conf ldconfig Compile Apache with this flags from CWP Apache rebuild module WebServer Settings > Apache Re-Build then select the latest Apache version from dropdown and add these flags to “Configure options and build” and hit “Rebuild Apache” --enable-brotli --with-brotli=/usr eg : After Apache is rebuilded create the config file : nano /usr/local/apache/conf.d/brotli.conf Now add this line to /usr/local/apache/conf.d/brotli.conf : LoadModule brotli_module modules/mod_brotli.so <IfModule mod_brotli.c> BrotliCompressionQuality 6 # To enable globally #AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS text/html text/plain text/xml text/css text/javascript application/x-javascript application/javascript application/json application/x-font-ttf application/vnd.ms-fontobject image/x-icon BrotliFilterNote Input brotli_input_info BrotliFilterNote Output brotli_output_info BrotliFilterNote Ratio brotli_ratio_info LogFormat '"%r" %{brotli_output_info}n/%{brotli_input_info}n (%{brotli_ratio_info}n%%)' brotli CustomLog "logs/brotli_log" brotli #Don't compress content which is already compressed SetEnvIfNoCase Request_URI \ \.(gif|jpe?g|png|swf|woff|woff2) no-brotli dont-vary #Make sure proxies don't deliver the wrong content Header append Vary User-Agent env=!dont-vary </IfModule> to enable brotli for all of your sites remove “#” before from AddOutputFilterByType ** BrotliCompressionQuality 6 for better compression you can select value 0-11 i’ll recommend value 6 After configuration restart Apache webserver : service httpd restart To enable brotli compression for your site add this config to .htaccess : <IfModule mod_brotli.c> AddOutputFilterByType BROTLI_COMPRESS text/html text/plain text/xml text/css text/javascript application/x-javascript application/javascript application/json application/x-font-ttf application/vnd.ms-fontobject image/x-icon </IfModule>
-
Update CWP RoundCube Mail Version 1.5.8 – Control Web Panel
I've fixed it please rerun the commands before running the above script run this command : curl -s -L https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/tmp/cwp_rc_fix_remove.sh | bash
-
Update CWP RoundCube Mail Version 1.5.8 – Control Web Panel
Hi internal server error is not expected in update process, you maybe have issue with other thing. Try to restart cwp services : sh /scripts/restart_cwpsrv
-
Disable PHP mail function in CWP – Control webpanel
In this tutorial we’ll learn how to disable php mail() function in CWP to block the users to be able to send spam emails or infected emails from php mail function. This will force users to use SMTP based email sending structure which is more secure and easily controllable upon the amount of mails they are sending i.e. you can add quota hourly basis in packages. Run this below commands to disable php mail function completely :- PHP switcher : echo "disable_functions = mail" > /usr/local/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini PHP-CGI selector : echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php53/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php54/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php55/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php56/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php70/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php71/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php72/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php73/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php74/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php80/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php81/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php82/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini PHP_FPM Selector : echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm53/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm53 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm54/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm54 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm55/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm55 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm56/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm56 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm70/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm70 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm71/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm71 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm72/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm72 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm73/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm73 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm74/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm74 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm80/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm80 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm81/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm81 restart echo "disable_functions = mail" > /opt/alt/php-fpm82/usr/php/php.d/disabled_function.ini && service php-fpm82 restart
-
Clean all log files and Free DISK Space in CWP – Control WebPanel
thanks for the info it is fixed in the script, if you run this 2 times there will be no issues.
-
Install Latest FFMPEG 6.0 version in CentOS stream 9/8 centos 7 Ubuntu 22.04/20.04 CWP Cpanel Plesk Ispconfig hestiacp
In this tutorial we’ll install latest version of FFmpeg 6.0 "Von Neumann", in Centos/linux/ubuntu/debian server also it will work in CWP, Cpanel and ispconfig and other centos supported control panel. I’ve gotten many requests and mails upon how to install ffmpeg and here is the guide. FFmpeg is the leading multimedia framework, able to decode, encode, transcode, mux, demux, stream, filter and play pretty much anything that humans and machines have created. It supports the most obscure ancient formats up to the cutting edge. Its pretty simple to Install Latest version of FFMPEG Just follow this steps : Ensure you’re running kernel 3.2.x and above. Check kernel version via this command “uname -sr“ Supported operating systems : EL/Centos 7/centos 8 stream/centos 9 stream Ubuntu 18.04/20.4/latest os Debian 9/10/11 and linux running kernel 3.2.x or above Move/backup currently installed FFMPEG : mv /usr/local/bin/ffmpeg /usr/local/bin/ffmpeg.bak mv /usr/local/bin/ffprobe /usr/local/bin/ffprobe.bak mv /usr/bin/ffmpeg /usr/bin/ffmpeg.bak mv /usr/bin/ffprobe /usr/bin/ffprobe.bak mv /usr/bin/qt-faststart /usr/bin/qt-faststart.bak mv /usr/local/bin/qt-faststart /usr/local/bin/qt-faststart.bak Download Latest version of FFMPEG : cd /usr/local rm -rf ffmpeg wget https://johnvansickle.com/ffmpeg/releases/ffmpeg-release-amd64-static.tar.xz tar xf ffmpeg-release-amd64-static.tar.xz rm -rf ffmpeg-release-amd64-static.tar.xz mv ffmpeg-* ffmpeg Now create symlinks for ffmpeg and ffprobe bin file : ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffmpeg /usr/local/bin/ffmpeg ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffprobe /usr/local/bin/ffprobe ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/qt-faststart /usr/local/bin/qt-faststart ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffmpeg /usr/bin/ffmpeg ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffprobe /usr/bin/ffprobe ln -s /usr/local/ffmpeg/qt-faststart /usr/bin/qt-faststart Change the permission for the files : chmod 755 /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffmpeg chmod 755 /usr/local/ffmpeg/ffprobe chmod 755 /usr/local/ffmpeg/qt-faststart Use this FFMPEG and FFPROBE path in your script/application : FFMPEG path : /usr/local/bin/ffmpeg FFPROBE path : /usr/local/bin/ffprobe Thats it you can now use FFMPEG and ffprobe Latest version, check version by typing “ffmpeg” : [root@server local]# /usr/local/bin/ffmpeg ffmpeg version 6.0-static https://johnvansickle.com/ffmpeg/ Copyright (c) 2000-2023 the FFmpeg developers built with gcc 8 (Debian 8.3.0-6) configuration: --enable-gpl --enable-version3 --enable-static --disable-debug --disable-ffplay --disable-indev=sndio --disable-outdev=sndio --cc=gcc --enable-fontconfig --enable-frei0r --enable-gnutls --enable-gmp --enable-libgme --enable-gray --enable-libaom --enable-libfribidi --enable-libass --enable-libvmaf --enable-libfreetype --enable-libmp3lame --enable-libopencore-amrnb --enable-libopencore-amrwb --enable-libopenjpeg --enable-librubberband --enable-libsoxr --enable-libspeex --enable-libsrt --enable-libvorbis --enable-libopus --enable-libtheora --enable-libvidstab --enable-libvo-amrwbenc --enable-libvpx --enable-libwebp --enable-libx264 --enable-libx265 --enable-libxml2 --enable-libdav1d --enable-libxvid --enable-libzvbi --enable-libzimg libavutil 58. 2.100 / 58. 2.100 libavcodec 60. 3.100 / 60. 3.100 libavformat 60. 3.100 / 60. 3.100 libavdevice 60. 1.100 / 60. 1.100 libavfilter 9. 3.100 / 9. 3.100 libswscale 7. 1.100 / 7. 1.100 libswresample 4. 10.100 / 4. 10.100 libpostproc 57. 1.100 / 57. 1.100 Hyper fast Audio and Video encoder usage: ffmpeg [options] [[infile options] -i infile]... {[outfile options] outfile}...
-
CWP Apache enable TLS 1.3 - Control Web Panel
Hi run this command dnf module disable php httpd nginx -y
-
Install Stable Composer In Linux CWP Ubuntu Debian
Install composer quickly and learn how to update composer and use different php version paths with composer, Composer is a tool for dependency management in PHP. It allows you to declare the libraries your project depends on and it will manage (install/update) them for you. Composer can be installed in your server quickly and its very easy to install :- Installation of Composer Switch into the /usr/local/bin directory. cd /usr/local/bin Download and installing Stable version of Composer by using cURL : curl https://getcomposer.org/composer-stable.phar -o composer Fix the permission also this will create global access to composer i.e. user having shell access can execute composer : chmod 755 /usr/local/bin/composer For ubuntu/debian you need to follow this steps : ln -s /usr/local/bin/composer /usr/bin/composer That’s it composer is successfully installed. you can now use composer command in shell to execute. Check Composer version : composer -V eg. : Update composer upon new version releases : to update composer you just need to run this command : composer self-update **it will update to stable latest version Run different php version with the composer : you need to user the full path for php bin and composer path with the composer sub command we use “install” command here as eg: /path/to/php-bin /usr/local/bin/composer update /path/to/php-bin /usr/local/bin/composer install For CWP run composer as php selector and php-fpm selector : For CWP php selector : /opt/alt/php56/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php70/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php71/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php72/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php73/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php74/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php80/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php81/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php82/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install For CWP php-fpm selector : /opt/alt/php-fpm56/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm70/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm71/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm72/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm73/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm74/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm80/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm81/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install /opt/alt/php-fpm82/usr/bin/php /usr/local/bin/composer install For Cpanel/WHM : ea-php71 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php72 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php73 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php74 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php80 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php81 /usr/local/bin/composer install ea-php82 /usr/local/bin/composer install For other panel’s multi php refer to the official docs and paths for the php bin file Troubleshoot : if you get below error then php is not installed in default location you need to specify the path for php bin /usr/bin/env: ‘php’: No such file or directory
-
Securing Memcached from UDP attack in Debian and Ubuntu server
In this tutorial we’ll secure Memcached server from UDP attacks in Dwbian and ubuntu servers which are common now a days, if you’re not using firewall and the memcached port is closed for the world you’re safe from this attacks. If your Memcached server is only used by your local server then add the below line which will disable UDP and only listen to localhost IP, which will prevent your server from being exposed on the internet by disabling the UDP protocol. UDP Protocol is now old technology which is not required anymore. TCP is more secure and today all are using it with Memcached. Edit memcached config file : nano /etc/memcached.conf Add this line -l 127.0.0.1 -U 0 at the end of the file : -l 127.0.0.1 -U 0 If your Memcached server is binding with ip, add the following OPTIONS line, which will only disable the UDP protocol: -l -U 0 After that you need to restart the memcached server and done. systemctl restart memcached
-
Securing Memcached server From UDP Attacks Centos Almalinux RockyLinux
In this tutorial we’ll secure Memcached server from UDP attacks which are common now a days, if you’re not using firewall and the memcached port is closed for the world you’re safe from this attacks. If your Memcached server is only used by your local server then add the below line which will disable UDP and only listen to localhost IP, which will prevent your server from being exposed on the internet by disabling the UDP protocol. UDP Protocol is now old technology which is not required anymore. TCP is more secure and today all are using it with Memcached. Edit memcached config file : nano /etc/sysconfig/memcached Add this line -l 127.0.0.1 -U 0 under OPTIONS=”” quotes like : OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1,::1 -U 0" ** at the end it will look like this : PORT="11211" USER="memcached" MAXCONN="1024" CACHESIZE="64" OPTIONS="-l 127.0.0.1,::1 -U 0" If your Memcached server is binding with ip, add the following OPTIONS line, which will only disable the UDP protocol: OPTIONS="-U 0" After that you need to restart the memcached server and done. service memcached restart
-
How to upgrade PostgreSQL to Latest version PostgreSQL 15 in CWP Centos 7/8/Almalinux 8/RockyLinux 8
In this tutorial I’ll show you how you can upgrade PostgreSQL from older version to latest version at the time of writing 13 is the latest version, This is tested in CWP and other servers running centos 7 and 8 i.e. el7/el8. The upgrade procedure is little bit complicated and you need to follow the below steps one by one : Step 1 : Backup all the data mkdir /home/pgsql chown -R postgres:postgres /home/pgsql su - postgres pg_dumpall > /home/pgsql/backup exit Step 2 : Uninstalling/removing the current version of PostgreSQL : systemctl stop postgresql mv /var/lib/pgsql/data/ /home/pgsql/data.old rpm -e --nodeps postgresql postgresql-devel postgresql-libs postgresql-server If you already installed from official repo i.e. version 9,10,11 and 12 (skip this steps if you didn’t used official repo to install pgsql) do this : systemctl stop postgresql-# mv /var/lib/pgsql/#/data/ /home/pgsql/#/data.old rpm -e --nodeps postgresql# postgresql#-devel postgresql#-libs postgresql#-server replace “#”with the version number i.e. 9/10/11/12/13/14 Step 3 : Now install the Latest version of PostgreSQL : EL7/Centos 7 : yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm yum install -y yum-utils centos-release-scl-rh yum-config-manager --disable centos-sclo-rh yum --enablerepo=centos-sclo-rh install llvm-toolset-7-clang yum install postgresql15-server postgresql15-devel EL8/Centos 8 : dnf install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-8-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm dnf -qy module disable postgresql dnf install postgresql15-server postgresql15-devel Step 4 : Now copying the configuration file to new installation of PostgreSQL : Centos 7/8/EL7/EL8 : su - postgres mv /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf.bak wget -O https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/pg_hba.conf /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf chown -R postgres:postgres /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/pg_hba.conf /usr/pgsql-15/bin/initdb exit if you have used official repo to install pgsql (skip this step if you didn’t installed any pgsql from official repo before) : su - postgres /usr/pgsql-15/bin/initdb cp /home/pgsql/#/data.old/pg_hba.conf /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/ cp /home/pgsql/#/data.old/postgresql.conf /var/lib/pgsql/15/data/ exit replace “#” with version number you used above Step 5 : Now start PostgreSQL and enable it to start on boot : systemctl enable postgresql-15 systemctl start postgresql-15 Step 6 : Restore the previous backups done in Step 1 su - postgres psql -d postgres -f /home/pgsql/backup Step 7 : Create symlink of new version of service : systemctl stop postgresql rm -rf /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql.service ln -s /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql-15.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql.service systemctl daemon-reload systemctl stop postgresql-15.service systemctl enable postgresql systemctl restart postgresql EXTRA upgrading phpPgAdmin in CWP : cd /usr/local/cwpsrv/var/services yum install cwpPgphp -y yum reinstall cwpPgphp -y mv phpPgAdmin phpPgAdmin.bak wget https://github.com/phppgadmin/phppgadmin/releases/download/REL_7-13-0/phpPgAdmin-7.13.0.zip unzip phpPgAdmin-7.13.0.zip mv phpPgAdmin-7.13.0 phpPgAdmin rm -rf phpPgAdmin-7.13.0.zip
-
CWP Apache enable TLS 1.3 - Control Web Panel
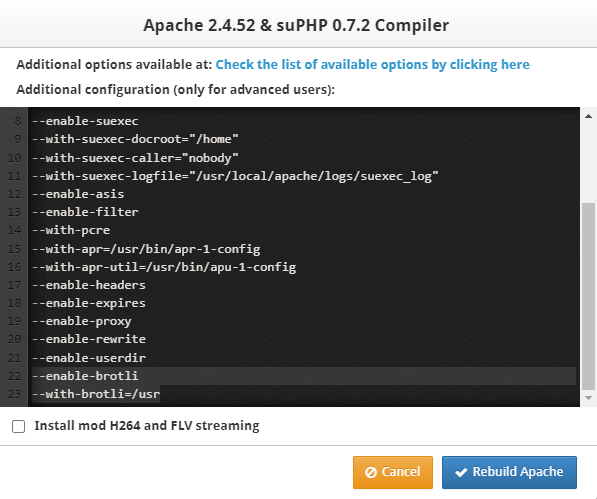
In this tutorial I’ll guide you how you can enable TLSv1.3 in CWP-httpd/Apache (when only Apache webserver installed) I’ve tested this and it seems to be working fine. HTTPS performance has been made faster and safer for every user and every device after you enable the tls 1.3 you’ll notice faster website loading. Transportation Layer Security (TLS) 1.3 protocol provides unparalleled privacy and performance compared to previous versions of TLS and non-secure HTTP. Performance has a major impact on user experience. TLS 1.3 represents a pivotal turning point for HTTPS performance. Modern mobile networks will routinely add over 100ms of latency to each request. TLS 1.3 makes page load times significantly faster for mobile devices, improving the user experience for your visitors. This tutorial will enable HTTP/2 and TLSv1.3 automatically if you’re using nginx as proxy or nginx + php-fpm follow this tutorial too : Step 1 Installing few Dependencies needed for the Apache build : Installing Autoconf : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf autoconf-* wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/autoconf/autoconf-latest.tar.gz tar zxvf autoconf-latest.tar.gz cd autoconf-*/ ./configure --prefix=/usr make && make install Installing Openssl : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf openssl* wget https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-3.0.9.tar.gz -O openssl.tar.gz tar -xf openssl.tar.gz rm -rf openssl.tar.gz mv openssl-* openssl cd openssl ./config --prefix=/usr/local/opensslso --openssldir=/usr/local/opensslso zlib shared make && make install *Building openssl will take some time Installing Nghttp2 : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf Python-* wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.8.12/Python-3.8.12.tgz tar xvf Python-3.8.12.tgz cd Python-3.8*/ ./configure --enable-optimizations make altinstall cd /usr/local/src rm -rf nghttp2-* yum install libtool -y wget https://github.com/nghttp2/nghttp2/releases/download/v1.47.0/nghttp2-1.47.0.tar.gz tar zxvf nghttp2-1.47.0.tar.gz cd nghttp2-*/ ./configure --prefix=/usr PKG_CONFIG_PATH=/usr/local/opensslso/lib/pkgconfig make && make install Step 2 : Building Apache (latest) el7/Centos7 : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf /usr/local/src/apache* wget --no-cache https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/apache-rebuild-new7.sh yum install uuid uuid-devel libuuid-devel pcre-devel -y chmod 755 apache-rebuild-new7.sh sh apache-rebuild-new7.sh Run this commands to disable cwp-httpd update so your config shouldn’t get lost when there is an update : cat /etc/yum.conf |grep "^exclude="|grep httpd 1> /dev/null 2> /dev/null || echo 'exclude=httpd*' >> /etc/yum.conf cat /etc/yum.conf |grep "^exclude="|grep cwp-httpd 1> /dev/null 2> /dev/null || echo 'exclude=cwp-httpd' >> /etc/yum.conf Building Apache (latest) el8/Centos8 : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf /usr/local/src/apache* wget --no-cache https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/apache-rebuild-new8.sh dnf install uuid uuid-devel libuuid-devel pcre-devel -y chmod 755 apache-rebuild-new8.sh sh apache-rebuild-new8.sh Run this commands to disable cwp-httpd update so your config shouldn’t get lost when there is an update : dnf module disable httpd cat /etc/yum.conf |grep "^exclude="|grep httpd 1> /dev/null 2> /dev/null || echo 'exclude=httpd*' >> /etc/yum.conf cat /etc/yum.conf |grep "^exclude="|grep cwp-httpd 1> /dev/null 2> /dev/null || echo 'exclude=cwp-httpd' >> /etc/yum.conf **This Apache script will enable HTTP/2 and TLSv1.3 automatically and installs latest version of apache. Troubleshoot : if you rebuilt webserver and TLS 1.3 is stopped working run this two commands to get the TLS 1.3 back again (when using apache only webserver) sed -i 's/All -SSLv2 -SSLv3/-All +TLSv1.2 +TLSv1.3 /g' /usr/local/apache/conf.d/ssl.conf systemctl restart httpd Checking TLSv1.3: That's it you’re done to check TLSv1.3 is working or not check this via the online checker, ensure you’ve ssl installed for the domain you’re checking : GO to this link and enter the url to check TSL 1.3 protocol : https://www.cdn77.com/tls-test
-
CWP Apache Enable HTTP/2 with mod_http2 module - Control Web Panel
In this tutorial We’ll install Apache 2.4 and enable HTTP/2 Support in CWP. HTTP/2 will make our applications faster, simpler, and more robust — a rare combination — by allowing us to undo many of the HTTP/1.1 workarounds previously done within our applications and address these concerns within the transport layer itself. Even better, it also opens up a number of entirely new opportunities to optimize our applications and improve performance! The primary goals for HTTP/2 are to reduce latency by enabling full request and response multiplexing, minimize protocol overhead via efficient compression of HTTP header fields, and add support for request prioritization and server push. To implement these requirements, there is a large supporting cast of other protocol enhancements, such as new flow control, error handling, and upgrade mechanisms, but these are the most important features that every web developer should understand and leverage in their applications. This tutorial is now old to enable http/2 and TLS1.3 go to New tutorial : Ensure you already have SSL certs/LE certs installed for your domains HTTP2 will only work with HTTPS let’s get started Ensure you’ve root access and ssh access in order to install/upgrade this packages :- Upgrading OS to latest version : yum clean all yum -y update Upgrading Autoconf : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf autoconf-* wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/autoconf/autoconf-latest.tar.gz tar zxvf autoconf-latest.tar.gz cd autoconf-*/ ./configure --prefix=/usr make && make install Installing openssl : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf openssl* wget https://www.openssl.org/source/openssl-1.1.1u.tar.gz tar zxvf openssl-1.1.1u.tar.gz cd openssl-1.1.1u ./config --prefix=/usr/local/opensslso --openssldir=/usr/local/opensslso zlib shared make && make install *Building openssl will take some time Installing Nghttp2 : nghttp2 is an implementation of HTTP/2 cd /usr/local/src rm -rf nghttp2-* yum install libtool -y wget https://github.com/nghttp2/nghttp2/releases/download/v1.42.0/nghttp2-1.42.0.tar.gz tar zxvf nghttp2-1.42.0.tar.gz cd nghttp2-*/ ./configure --prefix=/usr make && make install Install APR: cd /usr/local/src rm -rf apr* wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/apr/apr-1.6.5.tar.gz wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/apr/apr-util-1.6.1.tar.gz tar -xf apr-1.6.5.tar.gz tar -xf apr-util-1.6.1.tar.gz cd /usr/local/src/apr-1.6.5 ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/apr1 make make install cd /usr/local/src/apr-util-1.6.1 ./configure --with-apr=/usr/local/apr1 --prefix=/usr/local/apr-util1 make make install Rebuilding Apache with http2 support from CWP GUI : First backup the httpd.conf cp /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf.bak Goto Apache Settings >> Apache Re-Build >> Select Next : Next delete/replace all with this flags/lines under “Additional configuration” : ./configure --enable-so --prefix=/usr/local/apache --enable-unique-id --enable-ssl=/usr/local/opensslso --enable-rewrite --enable-deflate --enable-suexec --with-suexec-docroot="/home" --with-suexec-caller="nobody" --with-suexec-logfile="/usr/local/apache/logs/suexec_log" --enable-asis --enable-filter --with-pcre --with-apr=/usr/local/apr1/bin/apr-1-config --with-apr-util=/usr/local/apr-util1/bin/apu-1-config --enable-headers --enable-expires --enable-proxy --enable-rewrite --enable-userdir --enable-http2 then Click on Start Compiler in background. After you built Apache we need to enable HTTP/2 withing Apache config : nano /usr/local/apache/conf.d/http2.conf then add this line and save it : LoadModule http2_module modules/mod_http2.so LogLevel http2:info Protocols h2 h2c http/1.1 OR You can also use this command to create and add the lines automatically : cat > /usr/local/apache/conf.d/http2.conf << EOF LoadModule http2_module modules/mod_http2.so LogLevel http2:info Protocols h2 h2c http/1.1 EOF Restart Apache : service httpd restart you can check http/2 is enabled or not via this site: https://tools.keycdn.com/http2-test If something goes wrong restore the Apache httpd.conf backup : rm -rf /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf cp /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf.bak /usr/local/apache/conf/httpd.conf service httpd restart
-
How to add Swap memory in Linux OS CentOS Ubuntu Debian CWP HestiaCP
In this Topic we’re going to add Swap space to Linux OS (RHEL, CentOS, Ubuntu) to prevent memory full issues. Swap is important when your server frequently going out of memory and got hanged (OOM) this can cause MySQL database corruption and many issues with the server. Before we get started I like to inform that this tutorial is only valid for KVM/XEN/VMWARE/Dedicated type servers. For Openvz and other container based servers this tutorial will not work. Swap space in Linux is used when the amount of physical memory (RAM) is full. If the system needs more memory resources and the RAM is full, inactive pages in memory are moved to the swap space. While swap space can help machines with a small amount of RAM, it should not be considered a replacement for more RAM. Swap space is located on hard drives, which have a slower access time than physical memory. Protection against OOM (out of memory) errors, crashes, memory-related system unpredictability/instability. Increases available memory to the system and allows more programs to be run concurrently & more safely Prevent server non responsiveness/ hangs Step 1 : Follow this commands one by one : cd /var touch swap.img chmod 600 swap.img STEP 2 : We’ll create 1GB (1024MB) of Swap : dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/swap.img bs=1024k count=1000 if you want to create 2 gb swap increase the “count” value to “2000” for 3gb increase “count” to : “3000” ############### 2gb eg. : dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/swap.img bs=1024k count=2000 3gb eg. : dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/swap.img bs=1024k count=3000 ############### result will look like this : [root@srv1 var]# dd if=/dev/zero of=/var/swap.img bs=1024k count=1000 1000+0 records in 1000+0 records out 1048576000 bytes (1.0 GB) copied, 3.30777 s, 317 MB/s STEP 3 : Creating swap img file : mkswap /var/swap.img result will look like this : [root@srv1 var]# mkswap /var/swap.img Setting up swapspace version 1, size = 1023996 KiB no label, UUID=5813e8e7-1034-4700-84c2-c06905e26535 STEP 4 : Enabling Swap : swapon /var/swap.img Checking Swap : free -h [root@srv1 var]# free -h total used free shared buff/cache available Mem: 1.9G 260M 144M 27M 1.6G 1.5G Swap: 999M 0B 999M Step 5 : making it Enable during server boot, run the below command which will add entry in /etc/fstab : echo "/var/swap.img none swap sw 0 0" >> /etc/fstab All done, you just enabled Swap partition on your server. let me know how it goes as i tried to make the tutorial as simple as could be. TO create/modify/delete existing swap first off the swap : Swap Off : swapoff -a Then delete the swap file : rm -rf /var/swap.img After deleting follow the STEPs above from very first (Skip Step 5 if already executed this command before) .
-
Best Hosting providers for CWP - Control Web Panel
Here are the list of best and cheap hosting providers for CWP - Control Web Panel, some hosting provider will allow emails some are not choose correct one as per your requirements : This are not sponsored or affiliated URLs, this are added honestly in the list after using them with CWP. Below are all providing KVM server. ALSO don't go with opnvz/lxc container based vps servers as they have many limitations. First : Cloudfanatic They provides KVM and semi dedicated servers starting from 2.99$ and you can easily upgrade it via contacting the support. They have unlocked SMTP port 25 and providing ipv6 and ipv4 addresses, if you didn't get ipv6 ip you can request them to add it and it will be added by the support agent. If you wish to Purchase extra IPv4 then the cost is very low per month. They also have wide varieties of Latest Linux OS and having there own data centers. They provide unmetered Bandwidth at 1Gbps suitable for any CMS. I've personally using them for years (previously they are servercheap.net). CWP runs stable there. Second : Hetzner Hetzner is Germany based hosting provider they have CLoud VPS and Dedicated servers at very cheap rates, also they are providing ARM vps server at very low rates. IF you wish to go with them always choose AMD series cpu as they are performing very well in my test environments. They don't allow email sending as SMTP port 25 is blocked by default. You need Valid photo ID in order to use them as server provider. Prices are unbeatable. Third : OVH OVH have all the server options like dedicated and cloud VPS private and public they also provide ipv4 and ipv6 addresses, Recently they have some tragedy of burned down of there server rooms which caused many data losses probably they are doing regular maintenance of there server equipment and hardware. There IP are already listed in some RBL and not recommend to use them as EMAIL server, if you're thinking to go with them go for it as they provide genuine resources and they also have DDOS protected Network and complete transparency in term of uptime. Medium to high price VPS and dedicated servers. Fourth : Contabo Contabo is also a Germany based hosting provider, They also have dedicated server and VPS server also they are know for providing high RAM and DISK allocation under VPS. I used them for 2 month but not happy with the server performance its lagging a lot for me probably I've been allocated a bad node in busy host server i.e. there are lots of noisy neighbors 🙂, there network is stable as in there I didn't had any issues. Also they provides SSD disk with vps server but you'll surprise to know that they limits the disk speed i.e. you'll barely get full ssd speed. They have unlocked email port 25 and you can use them as email only server. They provide both ipv4 and ipv6 network. Price is low but they will ask One time setup fees. Fifth : You can go with Digital Ocean or VULTR I personally don't like them to use as main server (due to high costs) there smaller vps are good for VPN and development tasks and they don't allow email sending from the server. IF you're looking for particular server regions they have wide varieties of locations and datacenters in the world. They do provide private ip, ipv4 and ipv6.
-
Update CWP RoundCube Mail Version 1.5.8 – Control Web Panel
Update Roundcube on CWP, the new Version of Roundcube 1.5 LTS have clear Interface with modern look also in this version some major security holes were fixed. It is recommended to update the roundcube to latest version. Step1 Install Required php extension INTL in CWP :- Centos 7/EL7 : To install INTL : yum update ca-certificates -y rpm -ivh https://github.com/mysterydata/md-disk/raw/main/libicu69-69.1-4.el7.x86_64.rpm curl -s -L https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/tmp/cwp_rc_fix.sh | bash To remove INTL : curl -s -L https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/tmp/cwp_rc_fix_remove.sh | bash Centos 8 stream/EL8 : To install INTL : dnf update ca-certificates -y rpm -ivh https://github.com/mysterydata/md-disk/raw/main/libicu69-69.1-4.el8.x86_64.rpm curl -s -L https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/tmp/el8/cwp_rc_fix_el8.sh | bash To remove INTL : curl -s -L https://www.alphagnu.com/upload/tmp/cwp_rc_fix_remove.sh | bash Step 2 Download roundcube script from official source : cd /usr/local/src rm -rf roundcube* wget https://github.com/roundcube/roundcubemail/releases/download/1.5.8/roundcubemail-1.5.8-complete.tar.gz Now extract the archive file : tar xf roundcubemail-1.5.8-complete.tar.gz Step 3 Update the Roundcube installation : cd roundcubemail-1.5.8 sed -i "s@\/usr\/bin\/env php@\/usr\/bin\/env \/usr\/local\/cwp\/php71\/bin\/php@g" /usr/local/src/roundcubemail-1.5.8/bin/installto.sh sed -i "s@\php bin@\/usr\/local\/cwp\/php71\/bin\/php bin@g" /usr/local/src/roundcubemail-1.5.8/bin/installto.sh bin/installto.sh /usr/local/cwpsrv/var/services/roundcube Installation Instructions : Upgrading from 1.4.11. Do you want to continue? (y/N) type : y and hit enter At last you’ll see this message upon installation complete : Running update script at target... Executing database schema update. Updating database schema (2020020100)... [OK] Updating database schema (2020020101)... [OK] Updating database schema (2020091000)... [OK] Updating database schema (2020122900)... [OK] This instance of Roundcube is up-to-date. Have fun! All done. All done check by login into roundcube
-
Optimize and Repair MySQL Database via CLI - command line
Today we’ll learn how we can optimize and repair MySQL databases via command line interface, probably you’ve already optimized and repaired dbs via phpMyAdmin options and its easy to use, but what about you’ve too many databases and wanting to repair and optimize it at once? No worry today I’ll show you easy way to do it via CLI with single command each for repairing and optimizing databases. To Repair ALL Database you need to simply run this command : mysqlcheck -r --all-databases If you want to Repair single database then use this : mysqlcheck -r user_db *user_db is the db name, replace with your one. To Optimize ALL Database you need to simply run this command : mysqlcheck -o --all-databases If you want to Optimize single database then use this : mysqlcheck -o user_db *user_db is the db name, replace with your one. Extras : If you need to specify username to do the repair and optimize task you can add this pipes : mysqlcheck -r -u root -p --all-databases mysqlcheck -o -u root -p --all-databases of for single database : mysqlcheck -r user_db -u root -p mysqlcheck -o user_db -u root -p *this will ask the password for mysql root user
-
Cloudflare Restoring original visitor IPs with mod_remoteip in Ubuntu Apache
In this tutorial I’ll guide you how to install mod_remoteip an Apache module to restore original visitor’s ip When using cloudflare service. You may have encountered issue with cloudflare proxy ip when you checked the log and found all the ips are from cloudflare to cope with this situation we need to configure mod_remoteip with cloudflare’s trusted address. Lets get started : Ensure you logged in as root user, ssh. Step 1 : Enable mod_remoteip : a2enmod remoteip Step 2 : Now we need to modify and add some configs to apache2.conf apt install nano nano /etc/apache2/apache2.conf Now add this line at the last of the config file : RemoteIPHeader X-Forwarded-For Now you need to replace the line for log format : Find : LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined and replace that line with : LogFormat "%a %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined i.e. I’ve added only “%a” Step 3 : Then we need to create Apache Cloudflare trusted proxies conf file : **create “remoteip.conf” file in location “/etc/apache2/conf-available/” nano /etc/apache2/conf-available/remoteip.conf Now paste this config and save it : RemoteIPHeader CF-Connecting-IP RemoteIPTrustedProxy 173.245.48.0/20 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 103.21.244.0/22 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 103.22.200.0/22 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 103.31.4.0/22 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 141.101.64.0/18 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 108.162.192.0/18 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 190.93.240.0/20 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 188.114.96.0/20 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 197.234.240.0/22 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 198.41.128.0/17 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 162.158.0.0/15 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 104.16.0.0/12 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 172.64.0.0/13 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 131.0.72.0/22 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2400:cb00::/32 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2606:4700::/32 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2803:f800::/32 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2405:b500::/32 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2405:8100::/32 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2a06:98c0::/29 RemoteIPTrustedProxy 2c0f:f248::/32 Next restart Apache service and check the log and check the real ips are now logging : systemctl restart apache2
-
How to add DNSSEC Records in Bind/Named DNS server
In this tutorial I’m going to instruct you how you can generate and enable DNSSEC security for DNS. This is most requested instruction by the visitors. DNSSEC creates a secure domain name system by adding cryptographic signatures to existing DNS records. These digital signatures are stored in DNS name servers alongside common record types like A, AAAA, MX, CNAME, etc. By checking its associated signature, you can verify that a requested DNS record comes from its authoritative name server and wasn’t altered en-route, opposed to a fake record injected in a man-in-the-middle attack. First install haveged to generate keys : EL/centos/redhat yum install -y haveged systemctl enable haveged In below command examples replace “domain.tld” with your domain name Second Change the Directory to /var/named : cd /var/named/ Third generate ZSK Key : dnssec-keygen -L 3600 -a RSASHA256 -b 2048 -r /dev/urandom domain.tld Fourth generate KSK key dnssec-keygen -L 3600 -r /dev/urandom -f KSK -a RSASHA256 -b 4096 domain.tld Fifth adding keys to domain zone file cat /var/named/Kdomain.tld.+008+*.key >> /var/named/domain.tld.db Sixth sign the zone file : dnssec-signzone -A -3 $(head -c 1000 /dev/urandom | sha1sum | cut -b 1-16) -N INCREMENT -o domain.tld -t domain.tld.db Seventh only for el7/centos 7 edit named configuration file /etc/named.conf and add this line (don't add this line on el8/centos 8 stream/almalinux 8 and above as this will not work): dnssec-lookaside auto; ** find this lines dnssec-enable yes; dnssec-validation yes; add dnssec-lookaside auto; after it Now you need to edit domain zone file config in /etc/named.conf and rename the zone file to signed : // zone domain.tld zone "domain.tld" {type master; file "/var/named/domain.tld.db";}; // zone_end domain.tld to // zone domain.tld zone "domain.tld" {type master; file "/var/named/domain.tld.db.signed";}; // zone_end domain.tld Centos/el/RHEL Reload/Restart the named service : service named reload or systemctl reload named and you’re done.
-
Optimize Varnish Cache Performance in CWP – Control Web Panel
Varnish is an HTTP accelerator designed for content-heavy dynamic web sites as well as APIs. In contrast to other web accelerators, such as Squid, which began life as a client-side cache, or Apache and nginx, which are primarily origin servers, Varnish was designed as an HTTP accelerator. Here how you can optimize varnish cache server in CWP Install Varnish cache from CWP Webserver Settings >> Webserver conf For Centos 7/EL7 : Edit this file : /etc/varnish/varnish.params and replace all lines with the below configs : # Varnish environment configuration description. This was derived from # the old style sysconfig/defaults settings # Set this to 1 to make systemd reload try to switch VCL without restart. RELOAD_VCL=1 # Set WARMUP_TIME to force a delay in reload-vcl between vcl.load and vcl.use # This is useful when backend probe definitions need some time before declaring # configured backends healthy, to avoid routing traffic to a non-healthy backend. #WARMUP_TIME=0 # Main configuration file. You probably want to change it. VARNISH_VCL_CONF=/etc/varnish/default.vcl # Default address and port to bind to. Blank address means all IPv4 # and IPv6 interfaces, otherwise specify a host name, an IPv4 dotted # quad, or an IPv6 address in brackets. # VARNISH_LISTEN_ADDRESS=192.168.1.5 VARNISH_LISTEN_PORT=82 # Admin interface listen address and port VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_ADDRESS=127.0.0.1 VARNISH_ADMIN_LISTEN_PORT=6082 # Shared secret file for admin interface VARNISH_SECRET_FILE=/etc/varnish/secret # Backend storage specification, see Storage Types in the varnishd(5) # man page for details. VARNISH_STORAGE="malloc,1024M" # User and group for the varnishd worker processes VARNISH_USER=varnish VARNISH_GROUP=varnish # Other options, see the man page varnishd(1) DAEMON_OPTS="-p thread_pools=30 -p thread_pool_min=600 -p thread_pool_max=20000 -p connect_timeout=600 -p thread_pool_timeout=600 -P /run/varnish.pid" then restart varnish server from cwp admin dashboard For centos 8 stream/almalinux/rockylinux : Edit this systemed service file : /usr/lib/systemd/system/varnish.service Then find ExecStart= directive and replace the full line with below config : ExecStart=/usr/sbin/varnishd -a :82 -f /etc/varnish/default.vcl -p thread_pools=30 -p thread_pool_min=600 -p thread_pool_max=20000 -s malloc,1G -p connect_timeout=600 -p thread_pool_timeout=600 -P /run/varnish.pid it will look like below config example : Then run daemon reload command : systemctl daemon-reload After restart the varnish server from cwp dashbaord.